Something we need to know
Our sink faucets are a crucial part of our kitchen. The faucet is probably the most used piece of any home. The average American is using an average of 88 gallons of water daily – largely for cleaning hands. Currently, this workaholic product offers more prices than ever before. The Kitchen Faucet is available for from $3.o0 to $500.00 basis on different materials and finishing, although it’s recommended to spend more to ensure durability.
What material, finishing and types should be considered for a kitchen faucet?
- Types of faucet material
While faucets are manufactured in dozens of material combinations, the most common materials are brass, stainless steel, copper, zinc alloy, nickel, and plastic. The material will affect how the faucet functions even if the design does not define its appearance. Most materials will allow the most finishing on a surface. If you look closely at a kitchen tap you should understand the design. You could talk to a company if you aren’t t convinced. Test the weight of the faucet in an attempt to find out if the material is heavy (such as brass, lighter, or more flexible) (such as aluminum).
- Types of faucet finishing
What you do with your faucets is very important. Material and finishes can affect both the overall appearance and functionality as well as its durability and safety. Nowadays, the most popular finishings are chrome plating, stainless steel finish which is called BN finishing, matte black, PVD gold, etc. The finishing of the faucet is described in detail in the following article by HCdrink for your reference. https://hcdrinkwater.com/choose-kitchen-faucet-guide/
- Other factors for selecting a faucet
Then the model style, size, etc. The size of the stainless steel sink determines the place where faucets must be mounted if the spout is too big or small. Aim for the maximum height of the vent in spouts. It should ideally have an impressive height enough for cleaning the deepest spot, but not so high so the water can float around the sinks. Always make sure the area behind the faucet is easily cleaned to allow the handle to work. And the maintenance and so on. All are detailed in the above article link.
In this article, we focus on the analysis of faucet material that will have practical guidance for consumers to purchase, especially the company’s buyers.
- How to Choose the Best Material for Faucets
What About Materials?
Different metal finishes each have their own unique advantages when it comes to the resilience, cost, and design of the kitchen. Brass, steel, zinc, and plastic are all options for water faucet body materials.
1. Brass faucet

And of these faucets, the service life and performance as well as safety index together, then the best choice is the all-copper faucet, which has good corrosion resistance, anti-abrasion, easy processing, anti-bacterial, long service life, and other characteristics.
Antibacterial performance: copper can quickly kill super bacteria like MRSA in 30 minutes, and make bacteria that can not produce antibodies (copper faucet wall will not breed bacteria), which is other materials (such as stainless steel, plastic) that do not have the advantage.
Containing heavy metal elements.
The main material of the kitchen faucet currently used is brass HPb59, which contains trace amounts of lead. The current lead washing technology of the big brands can inhibit the precipitation of most heavy metals. For the United States’ lead-free copper requirements, copper faucets exported to the United States will be produced using lead-free copper.
2. Stainless Steel faucet
SS faucets do not contain lead and are acid- and alkali-resistant, do not suffer from corrosion, do not release harmful substances, and do not pollute the tap water source. Undoubtedly has become the focus of many faucet manufacturers began to focus on. It is understood that more than 304 stainless steel faucet surface does not need electroplating, its surface only needs polishing can be its stainless steel original color, and can continue to maintain the silver-white luster, never rust, stainless steel hardness, toughness is higher than copper products more than 2 times. Stainless steel hardness, toughness, soluble casting and cutting processing are much more difficult than copper, high cost.

3. Zinc faucets
Among the cheapest faucets are those made of zinc and zinc alloys. These are also the least durable of metal faucets.
Less expensive faucets may be manufactured using zinc alloy materials. The more well-known is the zMAC alloy created in 1929 by the New Jersey Zinc Companies to provide its metals. It was first made available for refinishing and reworking brass in applications where brass corrosion resistance wasn’t necessary. Generally used in the production of diecast products such as children’s toys and miniature trains. For faucets, zinc alloy is mainly used for the handle which doesn’t contact water directly.
Zinc belongs to heavy metal, corroded by the water will be mixed into the water, the human body has certain damage. Zinc alloy faucets and fittings are very easy to oxidation, underwater for a long time will be released under the immersion of zinc, lead, and other heavy metals harmful to humans, and the alloy will also become brittle if the pressure of the water is too large, very easy to burst. Direct contact with drinking water components, according to the regulations does not allow the use of zinc alloy materials.
Several reports say leads are more harmful than arsenic. Lead levels in drinking water are 5 ppb or a billion per year in the USA or Canada if the EPA does not have any regulations in place. Certainly, this might have taken some lead. According to the International Health Organization, the regulation would favor “no-lead” standards.

4. Plastic
Lastly, a plastic kitchen faucet will be the most inexpensive, and also the least durable. One positive aspect of plastic faucets, however, is that they are the only models that don’t contain lead.
Why is plastic faucet a problem?
Plastic faucet is generally PPR or PVC, these two faucets if the sun’s exposure for less than a year will decay, and plastic faucets exist stupid phenol exceeds the standard, long-term use of human health effects, headaches, diarrhea and other uncomfortable reactions.
- After the above analysis, I recommend choosing only copper faucets or stainless steel faucets, the following we have a detailed analysis of copper and stainless steel materials.
ORDINARY BRASS ROD

With excellent machinability, cold plasticity, hot plasticity, free cutting, and resistance to corrosion, it is easy to joint and braze.
LEAD-FREE ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION COPPER ROD

Lead-free environmental protection (Pb≤0.25%), Excellent mechanical properties, Excellent thermal processing performance, Good machining performance, Excellent resistance to stress corrosion
LEAD-FREE ENVIRONMENTALLY-FRIENDLY COPPER ROD

- Grade A polished copper ingots: the number of surfaces is impurities(the single area is less than or equal to 0.08 square mm)≤3
- DZR copper ingot: De-zinc-resistant depth requirements<100 microns
ANTI-DEZINCIFICATION COPPER ROD

Excellent resistance to dezincification, Excellent mechanical properties, Excellent thermal processing performance, Good machining performance, and excellent resistance to stress corrosion.
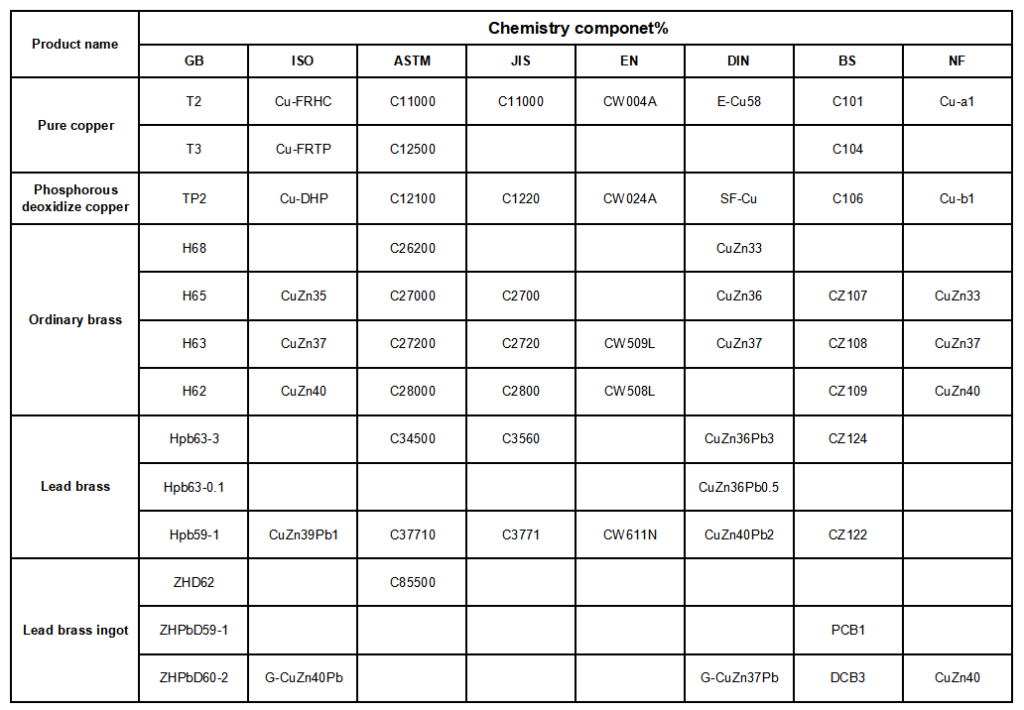
CHEMISTRY COMPONENT STANDARD
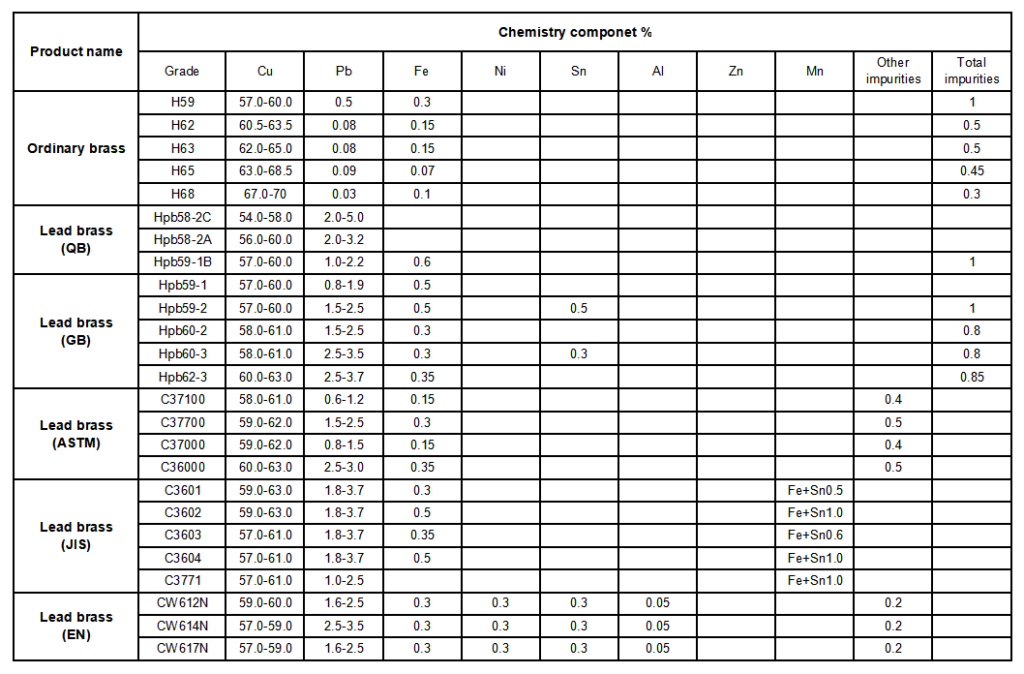
CHEMISTRY COMPONENT STANDARD
PRODUCT APPLICATIONS

HIGH-END BATHROOM
ACCESSORIES

ENVIRONMENTAL KITCHEN& BATHROOM
EQUIPMENT

VALVE

FITTINGS
TESTING EQUIPMENT


Brass Vs Stainless Steel

What’s The Difference?
It can be an overwhelming decision when it comes to choosing the perfect faucet for your home. Material, style function, and price all combine to make your choice extra tricky! Aside from wanting to be aesthetically pleasing, the primary importance is the quality and durability of your faucet. Brass and Stainless Steel are the two main streams of material used for faucet hardware on the market. Both options are highly beneficial and ensure a lifetime of function and satisfaction, but what is the main difference between them?
Material Composition (The Technical Stuff)
Brass is an alloy metal made of mostly copper and zinc. The composition can range anywhere between 50-63% copper and 50-37% zinc, with other additives used for material malleability. There are many manufacturing methods used to create brass hardware, including wrought, forged, cast, and die-cut processes. Since it has a relatively low melting point, it’s easier to cast and is soft enough to machine with little effort yet hardy enough to endure the rigors of life as a faucet. One of the main (and only) issues with brass faucets is that they’re not 100% lead-free. It used to be a common practice to add lead to brass for malleability purposes, but now it’s been virtually banned for use in faucets and most other plumbing fixtures. Before 2014, a faucet could contain as much as 8% lead and still call itself lead-free. Now the maximum lead content in a faucet is 0.25% (1/4 of 1%). To comply with the restrictions on lead, today’s faucet brass is “lead-free” brass that uses other additives for malleability.
304 and 316 stainless is another material option used for faucets. These stainless steel options contain 18% chromium and 8-10% nickel, the nickel giving the steel a particular crystalline structure to increase the material’s strength and malleability while the chromium helps the steel resist corrosion. A small amount of molybdenum (2-3%) is added to 316 steel to better resist acids. Both materials are austenitic steels, which means they are low- or non-magnetic. Stainless 304 is by far the more commonly-used alloy for making faucets, which is what our Lulani stainless steel faucets are made of. Stainless 316, known as marine grade stainless, has superior resistance to pitting, corrosion, and staining, particularly in acidic or salt environments, but comes in second behind Stainless 304 due to its hardness and manufacturing difficulty level. Stainless 316 is usually a bit more pricey than Stainless 304 because of this, but other than that they are virtually identical. In general, stainless steel is harder than brass and has a higher melting point, making it more difficult than brass to cast and machine.
Benefits
Brass is one of the oldest faucet materials around and is well-known for its durability since it can stand up to a lot of wear and tear. Brass faucets do not easily crack or disintegrate. It’s one of the most corrosion-resistant materials out there. This is particularly important if you have hard water, which corrodes a faucet even more quickly than other materials. It can almost always stand up to hot water damage and other corrosive environmental factors better than any other material. Brass is also fire resistant and often one of the few items salvaged when a home is razed by fire.
Since it’s so commonly used, it’s easy to find almost any plumbing part or fixture made of the same material, which makes replacing bathroom parts very easy. This can also make your installation and maintenance cost a little more cost-effective because the material is so easy to work with. Aside from being easier to find, brass fixtures are more malleable than steel or iron. This means it’s easier to bend, shape or mold fittings to suit your needs than most other metals.
Stainless steel, on the other hand, is considered a step above brass. Its physical durability exhibits longevity that other materials cannot muster. It has natural heat-resistant properties that are considered corrosion-resistant, tarnish-resistant, and will not rust. This means it requires less maintenance since it’s scratch-resistant and will disguise spots and smudges.
Stainless steel is extremely hygienic. It’s a common material used in the food processing, hospital, and pharmaceutical industries due to its corrosion and rust-resistant traits. The stainless steel material used in faucets provides a smooth, easy-to-clean surface that will not produce small pores or crevices where bacteria may otherwise harbor. Its naturally occurring properties can be very attractive features to a plethora of industries.
One of the major differences between brass and stainless steel material is that stainless steel is 100% lead-free. All plumbing fixtures in the US should be safe, but as we mentioned earlier, some materials contain a minute amount of lead. Stainless steel doesn’t, so you can rest assured it won’t release lead into the water that comes out of the faucet.
How To Tell What You’re Getting
You can coat most metal and plastic faucets and fixtures with almost any finish, which means when shopping for a new faucet, make sure to ask about what material is inside the faucet’s body. Another trick is to feel how heavy the faucet is. Since a good quality faucet will have some heft, you’ll want to feel how heavy various faucets are.
Solid brass constructions are much higher quality than faucets that have brass plating or a brass-like finish. You can usually distinguish between the two because solid brass is a lot heavier. The same goes for stainless steel fixtures. There are a lot of cheaper steel options on the market, but their lower price point often correlates with their lower quality. True stainless steel faucets are made of either 304 or 316 stainless, so be wary of anything listed differently.
